Suppose you want to predict the price of a house by just knowing about the size of the house. Although we know that there are other factors such as number of rooms, locality, etc which also affect the price but let’s consider the simple case only. So now to know the price, probably you will collect the price of houses of nearly similar size and will take the mean of the prices. This will be the prediction for the house. But collecting data for each size and taking mean is not convenient.
Here comes the need of regression to accomplish our task. So let’s see how !
Introduction
Regression is a very powerful Machine Learning technique which is used for estimating the value of a dependent variable called target variable and one or many independent variables called features or predictors. It is supervised learning technique ie. the data that we have for training the model is labeled and it provides the output that is continuous.
Regression is useful in following ways:
- It communicates the relationship between features and the target variable in a compact way.
- It predicts the values of target variable for unseen features.
- It can also be used to detect anomalies in the set of data points.
Types of Regression Techniques:
-
Univariate or Simple Linear Regression
-
Multivariate Linear Regression
-
Polynomial or Non-linear Regression
-
Logistic Regression
-
Lasso Regression
-
Ridge Regression
There are many kinds of regression techniques but we’ll be focusing on simple linear regression with two variables and a brief introduction to multiple linear regression.

Univariate Linear Regression
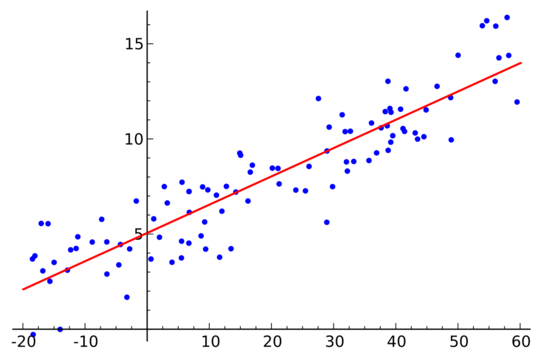
Simple Linear Regression
Univariate Linear Regression includes just one feature or predictor variable to predict the outcome variable. As the name suggest ‘linear’, the goal is to find a regression line which gives the relation between the feature and outcome. The general equation of a line is
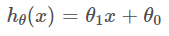 In the equation the theta_0 and theta_1 are coefficients which basically represent the intercept and slope of the regression line respectively. If we are able to find the values of theta_0 and theta_1 then we can easily predict the value h(x) for any value of x.
In the equation the theta_0 and theta_1 are coefficients which basically represent the intercept and slope of the regression line respectively. If we are able to find the values of theta_0 and theta_1 then we can easily predict the value h(x) for any value of x.
These x and y can be any values like if we have the x as height of a person then we can predict the weight of person as y after knowing the coefficients.
These coefficients are learned after training the model on training data (includes corresponding x’s and y’s).
So how to find the values of coefficients ?
The coefficients are chosen so that the error between predicted ŷ and real y gets minimized. The red line is the regression line and the points given are real y. The difference between the values of h(x) and y are called residuals which are shown by vertical lines.
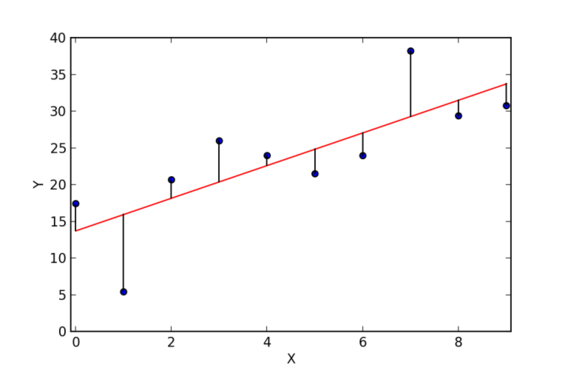
Now to minimize this error we use an algorithm called Gradient Descent.
Gradient Descent
To measure the error we introduce a cost function and minimize the error given by
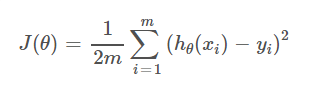
Here m is the number of data points in training data. We use calculus to minimize the error. We start with some theta_0 and theta_1 and keep changing them until we hopefully end up at minimum. To update the values of theta_0 and theta_1 we use the gradient descent algorithm which is given as
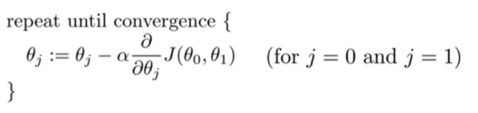
This will shift the coefficients more towards the minima with each iteration. Here alpha is the learning rate which is a hyperparameter and decides the rate at which the coefficients will be updated. Once reached at minima, the gradient will become zero and there will be no change in the coefficients. This will indicate that we have got our values for theta_0 and theta_1.
Another method to find the coefficients for univariate linear regression
First find out the correlation coefficient r by
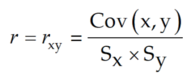
where cov(x,y) is the covariance of x and y. Sx and Sy are the standard deviation of x and y respectively. Then the slope b or theta_1 can be calculated by
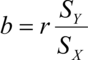
There is also a property that the linear regression line always passes through mean (x̄, ȳ ) of the given data (proof). We can use this to find the value of a or theta_0 by
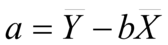
Multivariate Linear Regression
Multivariate Linear Regression is same as univariate linear regression but the number of features are two or more. It provides a line fitting the data which is multidimensional with the number of dimensions to be one more than the number of features. The equation of line is given by
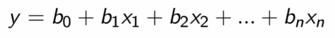
Here there are n number of features and b0 , b1 , …..bn are the coefficients. To find the coefficients we use the gradients descent algorithm.
The data is not always suitable to fit with a line. If there is non-linearity in the data then at that time we use polynomial regression ie. we use a higher order curve (generally quadratic or cubic) to fit the data.
I hope now you have a proper understanding of the Linear Regression and its working. However all this can be easily performed in python using the Scikit-Learn library. So get started :)
Thank you for reading !